Table Of Content
Now we are going to shift gears and look at factorial design in a quantitative approach in order to determine how much influence the factors in an experiment have on the outcome. As these researchers expected, participants who were lower in SES tended to give away more of their points than participants who were higher in SES. This is consistent with the idea that being lower in SES causes people to be more generous.
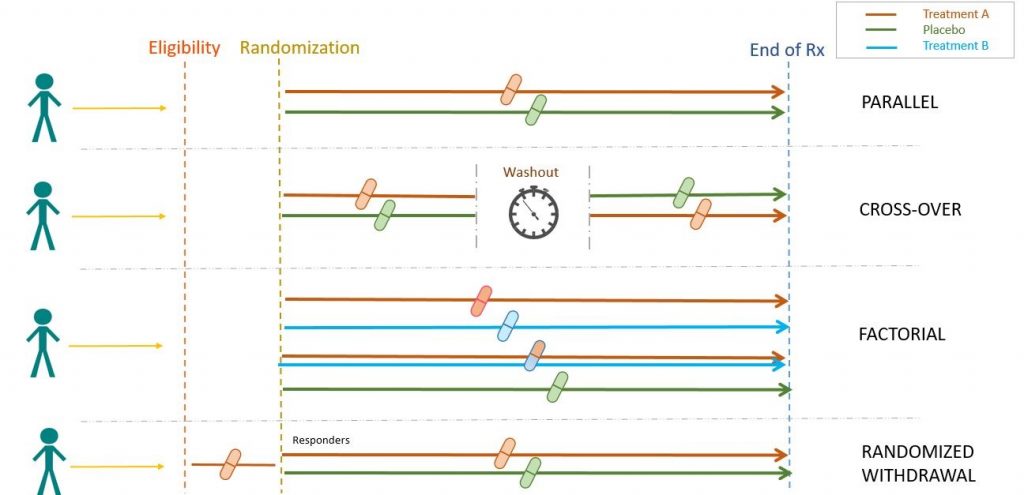
Implementing Clinical Research Using Factorial Designs: A Primer
These included health, knowledge of heart attack risk factors, and beliefs about their own risk of having a heart attack. They found that more optimistic participants were healthier (e.g., they exercised more and had lower blood pressure), knew about heart attack risk factors, and correctly believed their own risk to be lower than that of their peers. Time of day (day vs. night) is represented by different locations on the x-axis, and cell phone use (no vs. yes) is represented by different-colored bars. It would also be possible to represent cell phone use on the x-axis and time of day as different-colored bars. The choice comes down to which way seems to communicate the results most clearly.
Factorial Designs¶
In a between-subjects factorial design, all of the independent variables are manipulated between subjects. For example, all participants could be tested either while using a cell phone or while not using a cell phone and either during the day or during the night. This would mean that each participant was tested in one and only one condition. In a within-subjects factorial design, all of the independent variables are manipulated within subjects. All participants could be tested both while using a cell phone and while not using a cell phone and both during the day and during the night. The advantages and disadvantages of these two approaches are the same as those discussed in Chapter 4).
Characterization of industrial ceramic glazes containing chromite processing waste: Experimental factorial design ... - ScienceDirect.com
Characterization of industrial ceramic glazes containing chromite processing waste: Experimental factorial design ....
Posted: Fri, 15 Apr 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Non-Experimental Studies With Factorial Designs
One cannot discuss the results without speaking about both the type of fertilizer and the amount of water used. Using fertilizer A and 500 mL of water resulted in the largest plant, while fertilizer A and 350 mL gave the smallest plant. Fertilizer B and 350 mL gave the second largest plant, and fertilizer B and 500 mL gave the second smallest plant. There is clearly an interaction due to the amount of water used and the fertilizer present.
Factorial designs are the basis for another important principle besides blocking - examining several factors simultaneously. We will start by looking at just two factors and then generalize to more than two factors. Investigating multiple factors in the same design automatically gives us replication for each of the factors.
A new multi-factor multi-objective strategy based on a factorial presence-absence design to determine polymer additive ... - ScienceDirect.com
A new multi-factor multi-objective strategy based on a factorial presence-absence design to determine polymer additive ....
Posted: Tue, 18 Oct 2022 02:33:51 GMT [source]
Assigning Participants to Conditions
One of the limitations of case‐control studies is that they cannot estimate prevalence of a disease accurately as a proportion of cases and controls are studied at a time. Case‐control studies are also prone to biases such as recall bias, as the subjects are providing information based on their memory. Hence, the subjects with disease are likely to remember the presence of risk factors compared to the subjects without disease. In clinical research, our aim is to design a study which would be able to derive a valid and meaningful scientific conclusion using appropriate statistical methods. The conclusions derived from a research study can either improve health care or result in inadvertent harm to patients.
1.4. Measures of the Same Construct¶
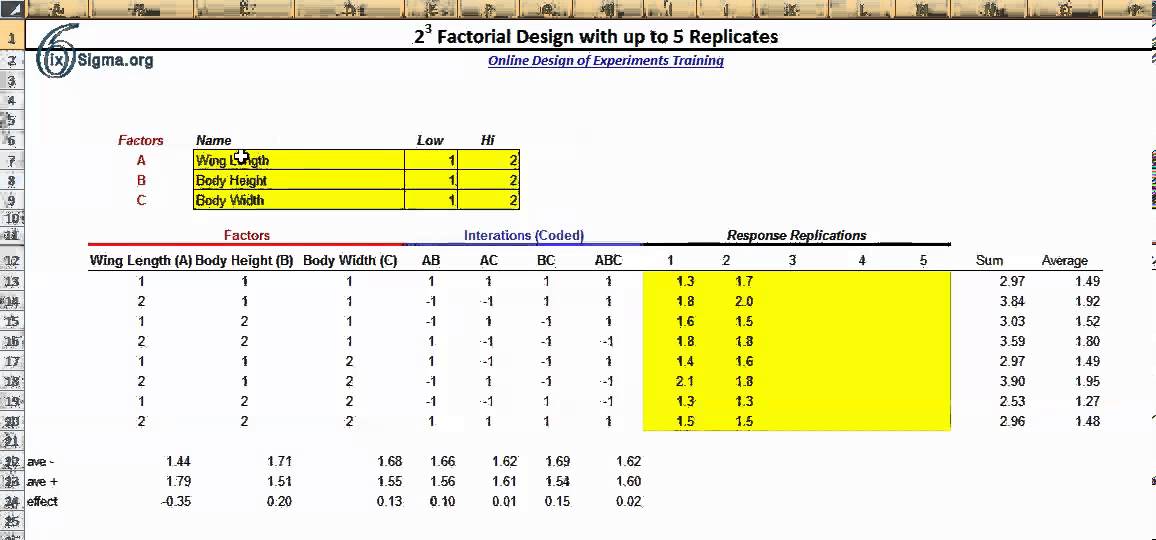
In addition to the above effects plots, Minitab calculates the coefficients and constants for response equations. The response equations can be used as models for predicting responses at different operating conditions (factors). The coefficients and constants for wt% methanol in biodiesel and number of theoretical stages are shown below.
Factorial Designs
In sum, in a factorial experiment, the effects, relative effects, and statistical significance of ICs will likely change depending upon the number and types of components that co-occur in the experimental design. This arises, in part, from the fact that the effects of any given factor are defined by its average over the levels of the other factors in the experiment. It is important, therefore, for researchers to interpret the effects of a factorial experiment with regard to the context of the other experimental factors, their levels and effects. This does not reflect any sort of problem inherent in factorial designs; rather, it reflects the trade-offs to consider when designing factorial experiments. When taking a general linear model approach to the analysis of data from RCTs and factorial experiments, analysts must decide how to code categorical independent variables.
4. Complex Correlational Designs¶
The presence of an interaction, particularly a strong interaction, can sometimes make it challenging to interpet main effects. For example, take a look at Figure 5.14, which indicates a very strong interaction. Kaplan et al1 found that, in study 1, light therapy alone did not change sleep timing. However, in the second study, light plus behavioral therapy significantly moved sleep onset approximately 50 minutes earlier, on average, and increased nightly sleep time by approximately 43 minutes.
An example of a case‐control study was performed in Pakistan evaluating the risk factors for neonatal tetanus. They retrospectively reviewed a defined cohort for cases with and without neonatal tetanus.9 They found a strong association of the application of ghee (clarified butter) as a risk factor for neonatal tetanus. Although this suggests a causal relationship, cause cannot be proven by this methodology (Figure 3). Alternatively, an investigator might modify an intervention when it co-occurs with a particular, second intervention component. For instance, assume that a design has three factors; two are medication factors (e.g., varenicline, on/off, in one factor and NRT product [nicotine patch vs. nicotine lozenge], in a second factor). The third factor is an adherence factor (i.e., an automated medication counter with counseling, on/off).
The sample size will help determine the number of strata that would need to be chosen for a study. Randomization is a well‐established methodology adopted in research to prevent bias due to subject selection, which may impact the result of the intervention/experiment being studied. It is one of the fundamental principles of an experimental study designs and ensures scientific validity. It provides a way to avoid predicting which subjects are assigned to a certain group and therefore, prevent bias on the final results due to subject selection. This also ensures comparability between groups as most baseline characteristics are similar prior to randomization and therefore helps to interpret the results regarding the intervention/experiment group without bias. Hence, the subjects are monitored over a period of time for occurrence of a particular disease process.
No comments:
Post a Comment